1. Basic definition of field terminal plug
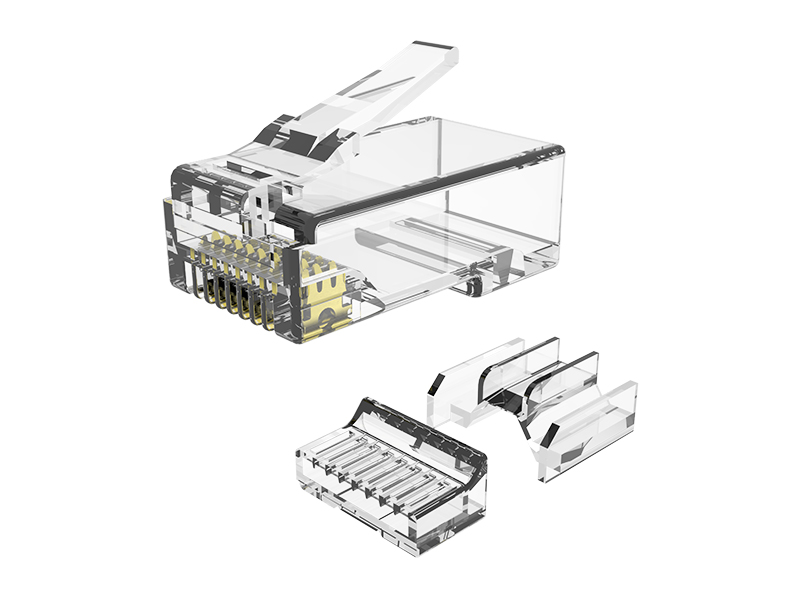
A connector directly installed during field construction, without the need for factory pre termination, and manually connected by construction personnel to the cable and plug.
Commonly used in wiring scenarios such as networking, industrial control, and security, it replaces the traditional "module+jumper" mode.
2. Core Features
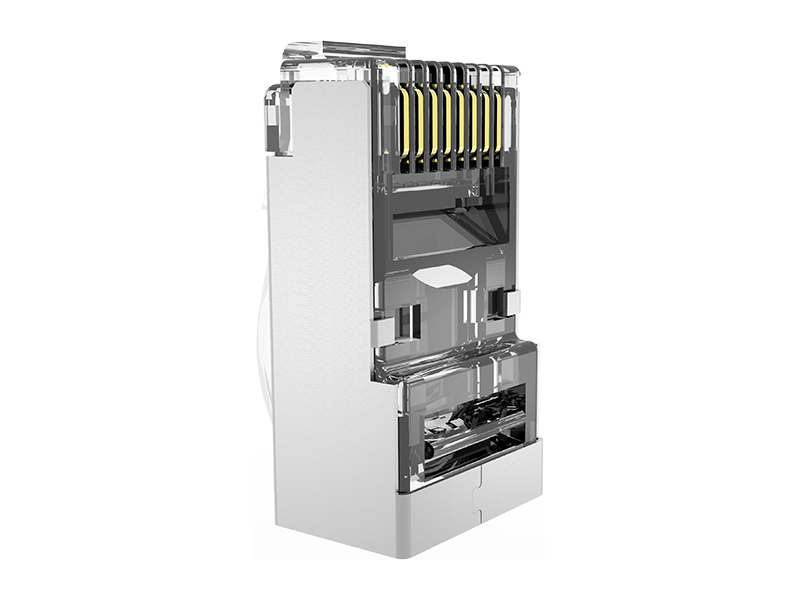
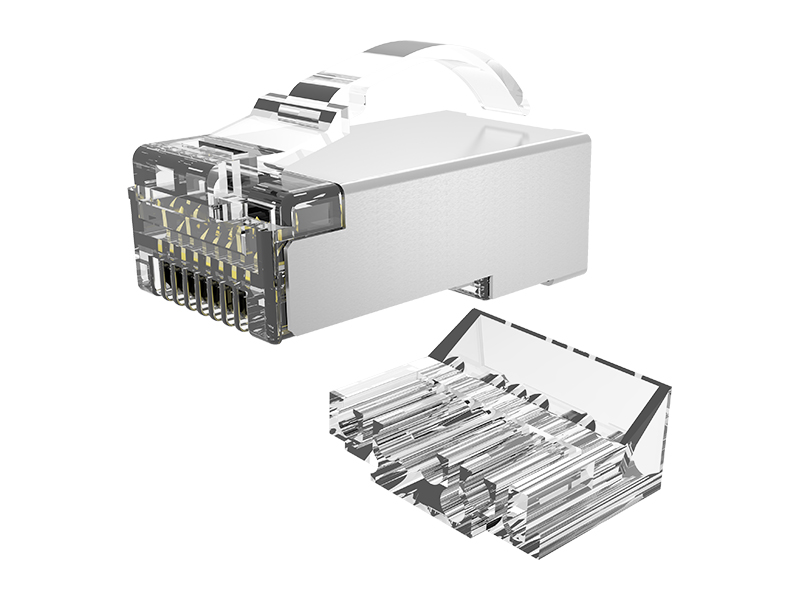
Ready to use: eliminates modular panels and jumpers, reduces link nodes, and improves reliability.
Flexible adaptation: Supports multiple wire diameters (such as thin jumper wires or thick trunk wires) to adapt to different installation environments.
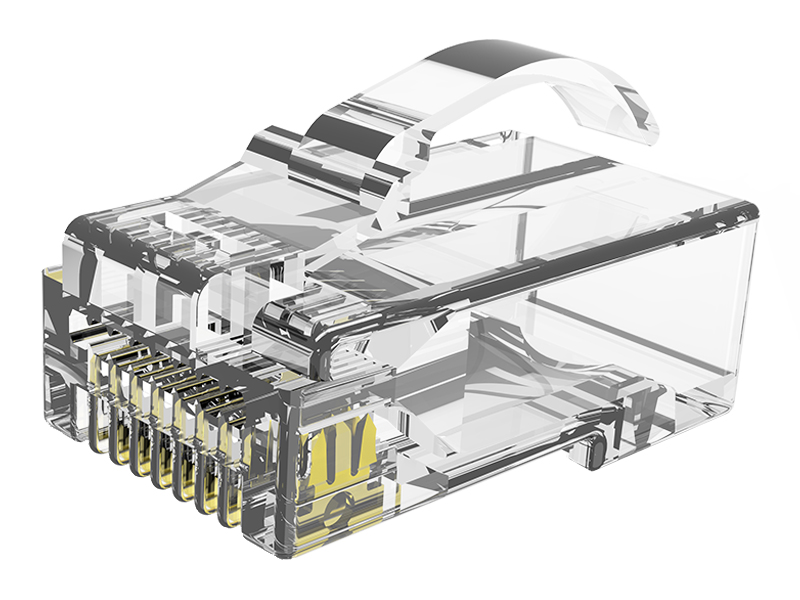
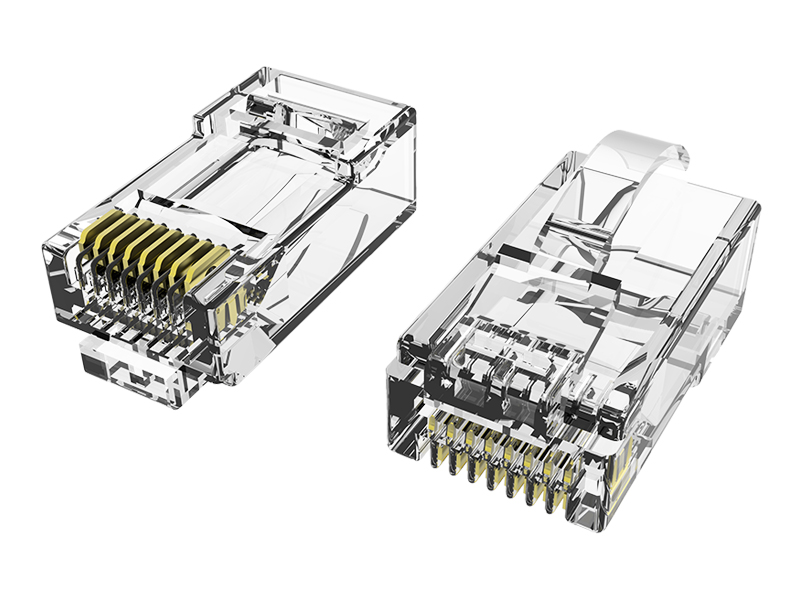
Special tools: It is necessary to use tools such as wire cutters and crimping pliers to complete the end connection, and some models can be operated repeatedly.
3. Typical application scenarios
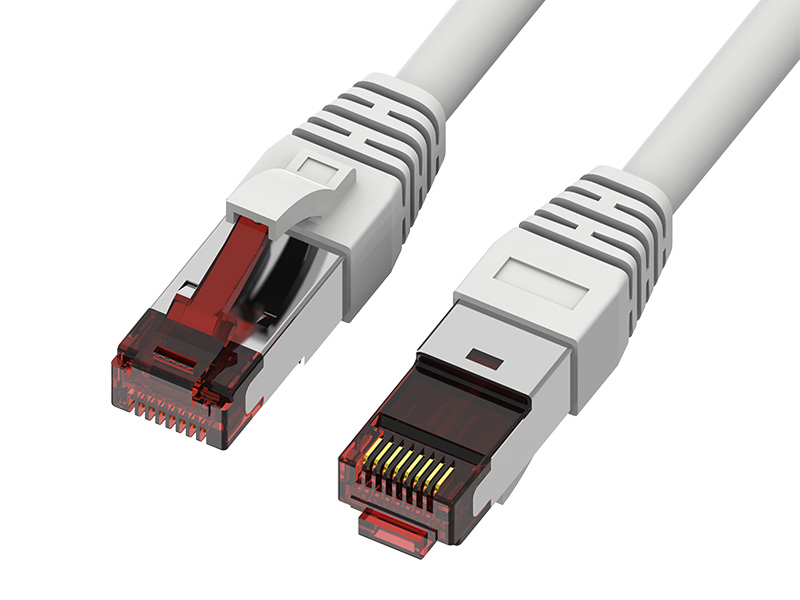
Network cabling: Direct cabling (MPTL topology) for devices such as PoE cameras and wireless APs.
Industrial site: rapid deployment and maintenance of equipment control cabinets and sensor signals.
Temporary cabling: Network construction for short-term high flexibility needs such as exhibitions and events.
4. Differences from traditional connection methods
Traditional method: cable → module (panel) → jumper → equipment, with many nodes and high losses.
On site termination: cable → plug → equipment, simplifying the link and reducing the failure rate.
5. Examples of main types
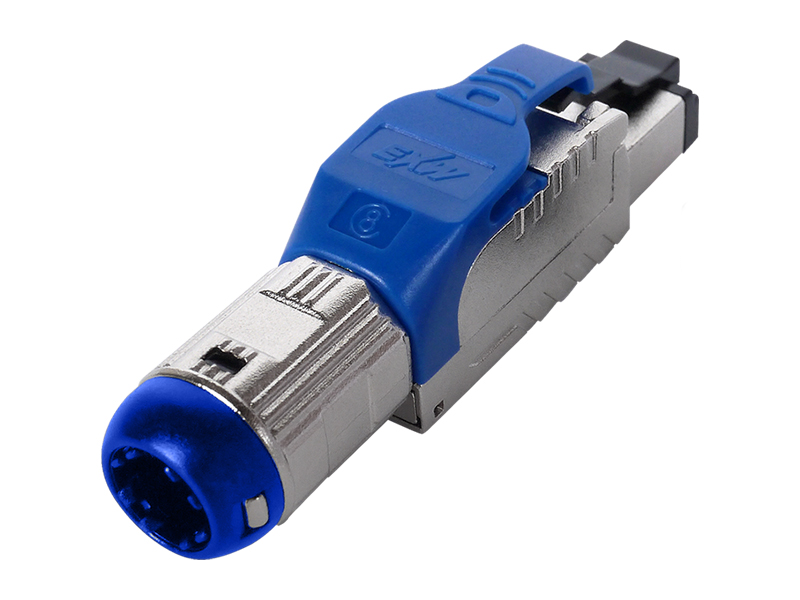
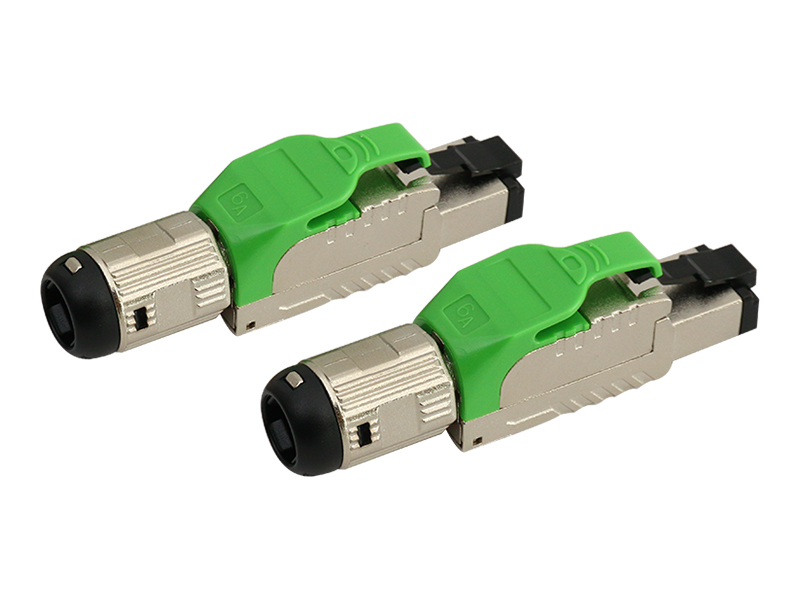
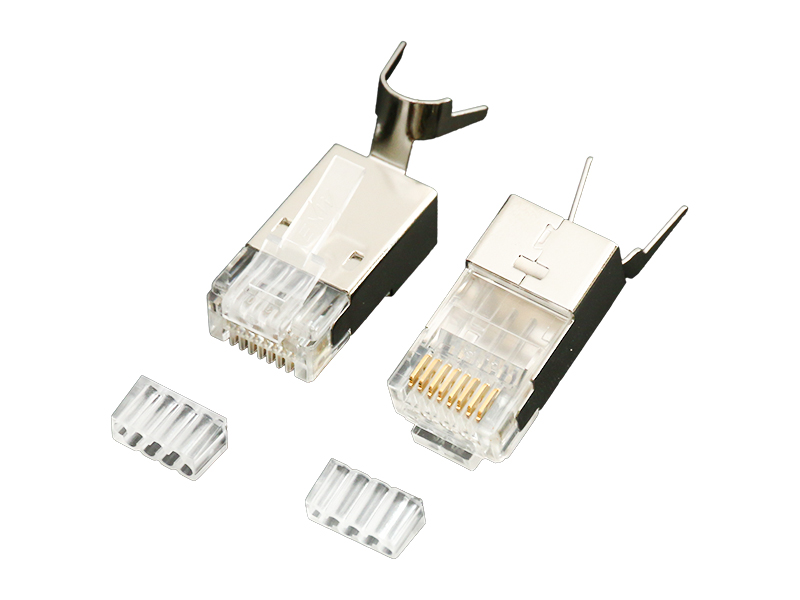
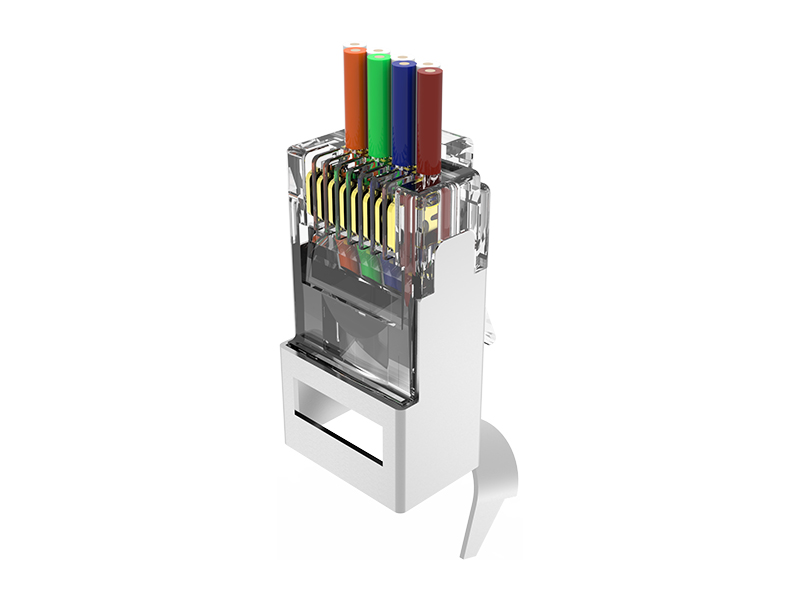
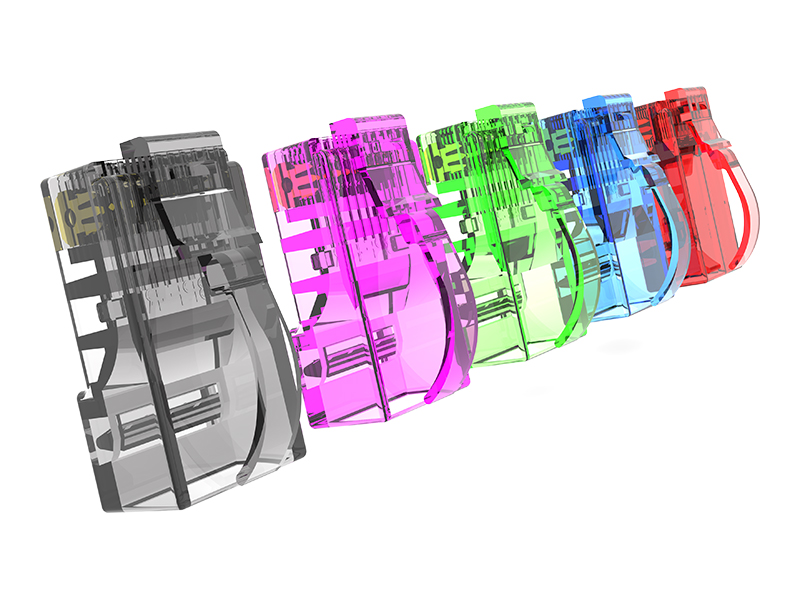
Network category: Cat.6A field termination RJ45 plug (with shielded/unshielded).
Industrial type: M12/M8 threaded locking field plug.
Special type: Fiber optic quick connector (field grinding type).
6. Precautions for use
High process requirements: Poor termination can easily lead to signal attenuation or contact failure.
Compatibility verification: It is necessary to match the cable type (such as shielded wire with shielded plug).
Environmental protection: Waterproof and dustproof models should be selected for outdoor/industrial scenes.
| Aspect | Description | Key Advantages | Important Notes |
| Definition | Connectors installed directly on cables during fieldwork, without factory pre-termination. | Eliminates need for patch panels/jumpers in direct-to-device connections. | Requires proper tools and technician skill for reliable installation. |
| Primary Use Cases | • Network cabling (PoE cameras, APs) • Industrial controls • Temporary installations | Simplifies链路 topology (MPTL model), reduces failure points. | Not all applications support MPTL - check standards first. |
| Common Types | • RJ45 plugs (Cat.5e/6/6A) • Industrial M12/M8 connectors • Fiber quick-connects | Accommodates various cable gauges and environments. | Shielded versions required for EMI-sensitive environments. |
| Installation Method | Uses IDC punch-down or crimping tools (varies by model). | Some designs allow re-termination if errors occur. | Poor termination causes signal loss - test every connection. |
| VS Traditional Links | Replaces: Cable → Jack → Patch Panel → Jumper → Device with Cable → Plug → Device | Fewer components = better signal integrity and space savings. | Requires compatible equipment ports (size/type). |
| Critical Considerations | • Termination skill • Shield continuity (if applicable) • Environmental ratings | Enables faster deployment in field conditions. | Industrial versions (IP67, vibration-proof) cost more but last longer. |



 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch عربى
عربى