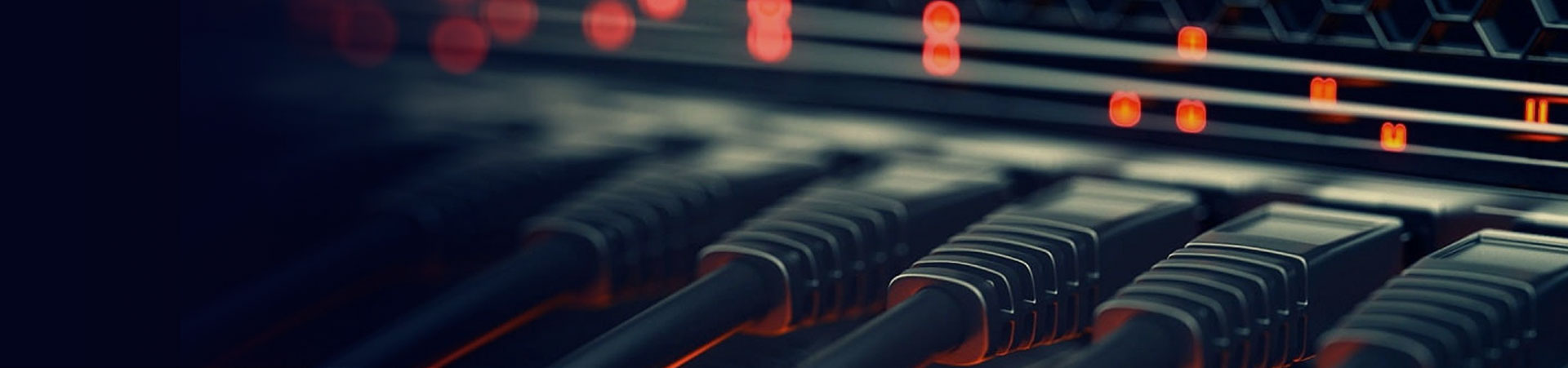
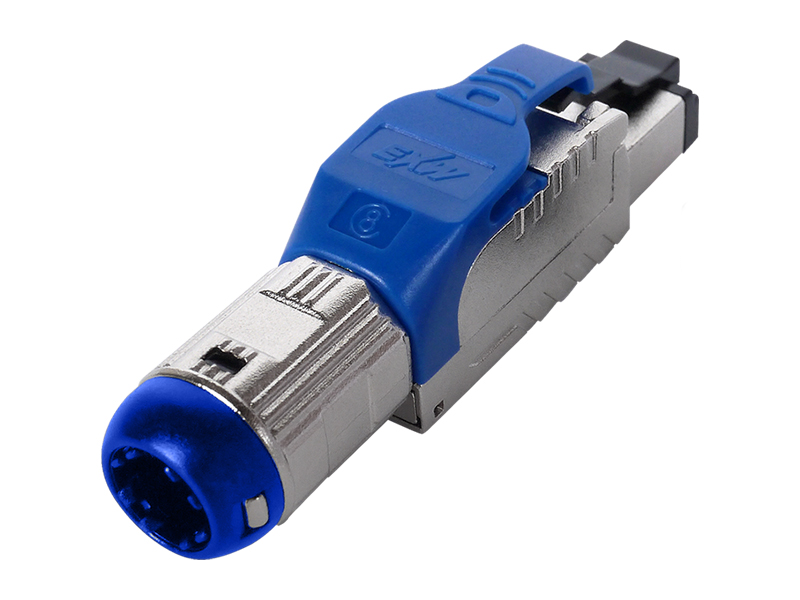
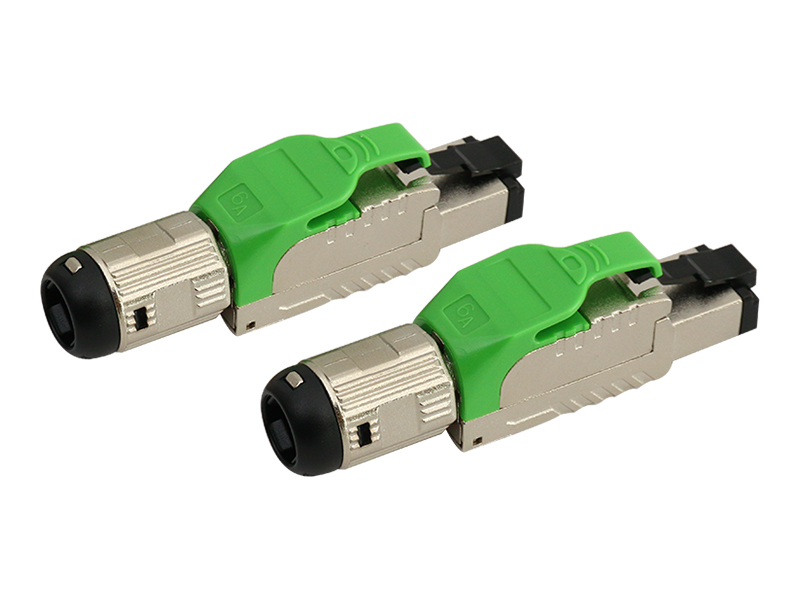
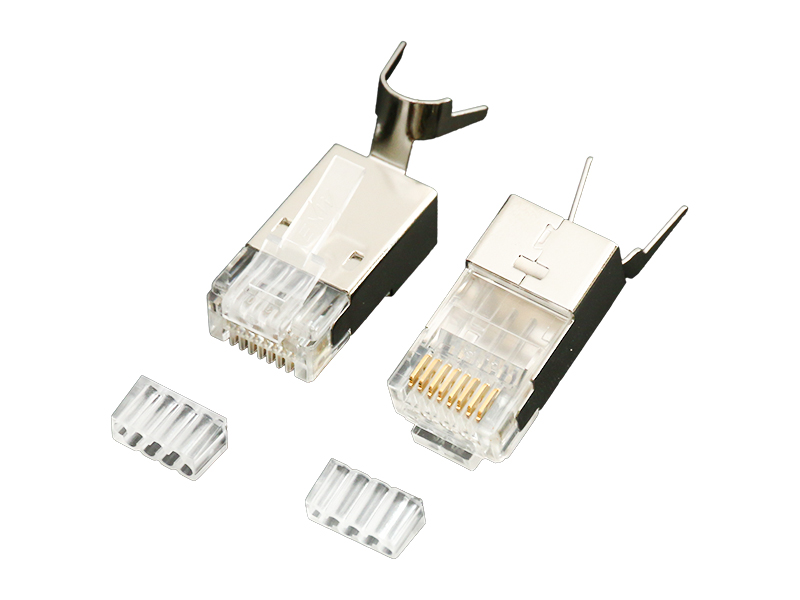
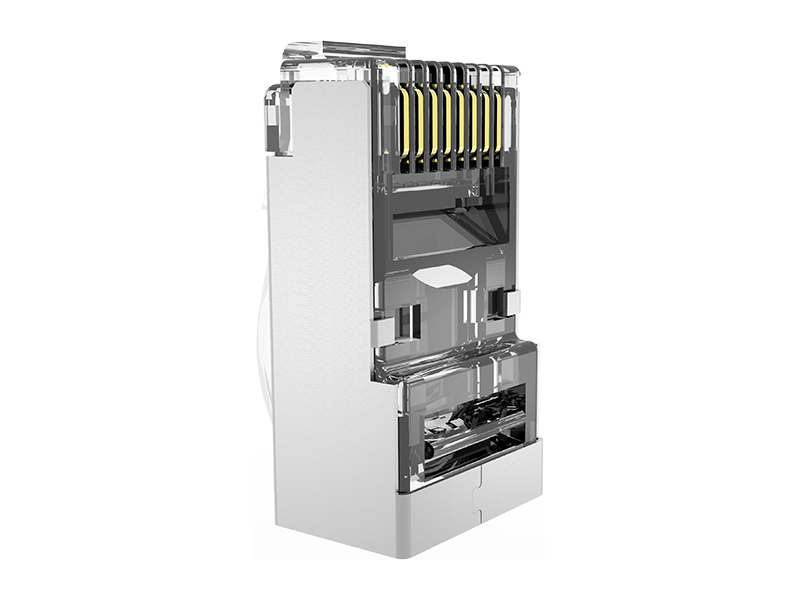
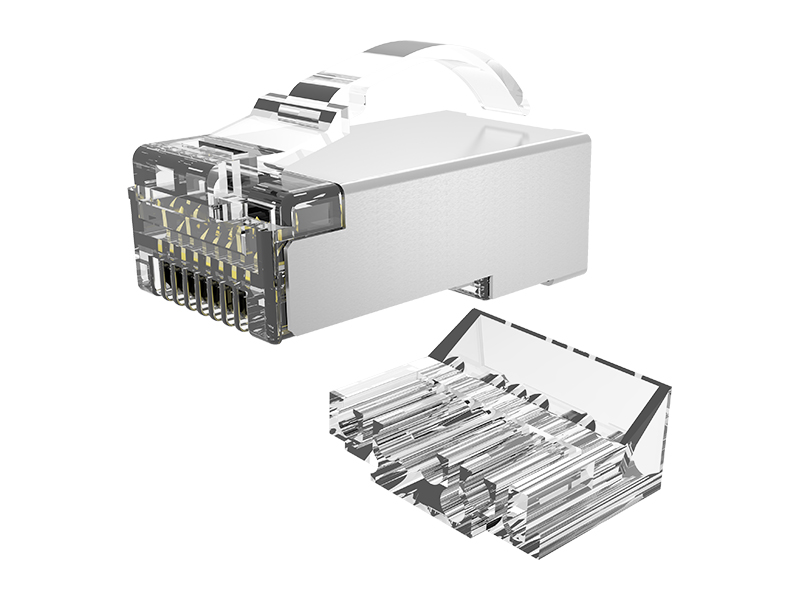
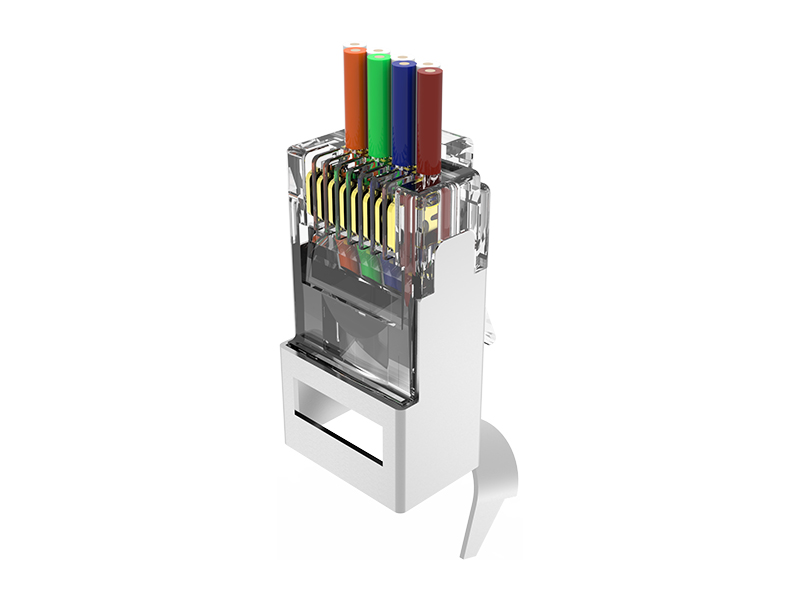
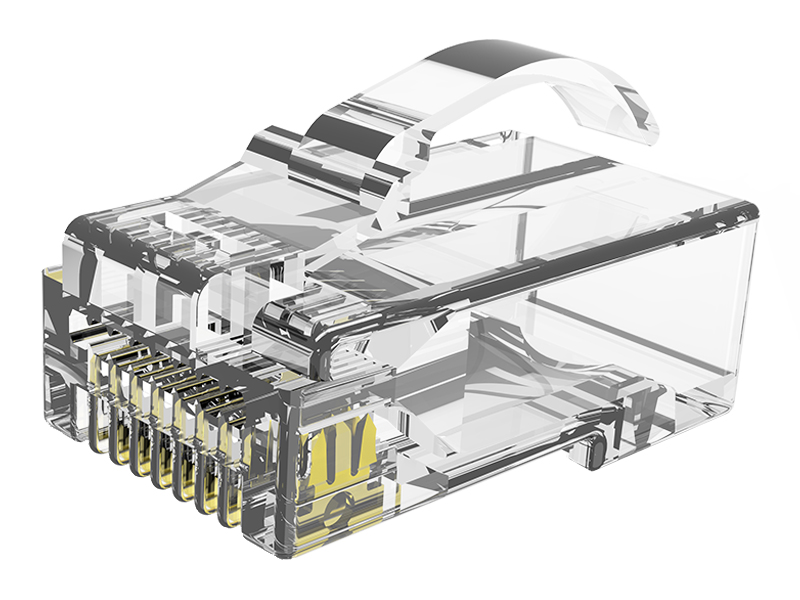
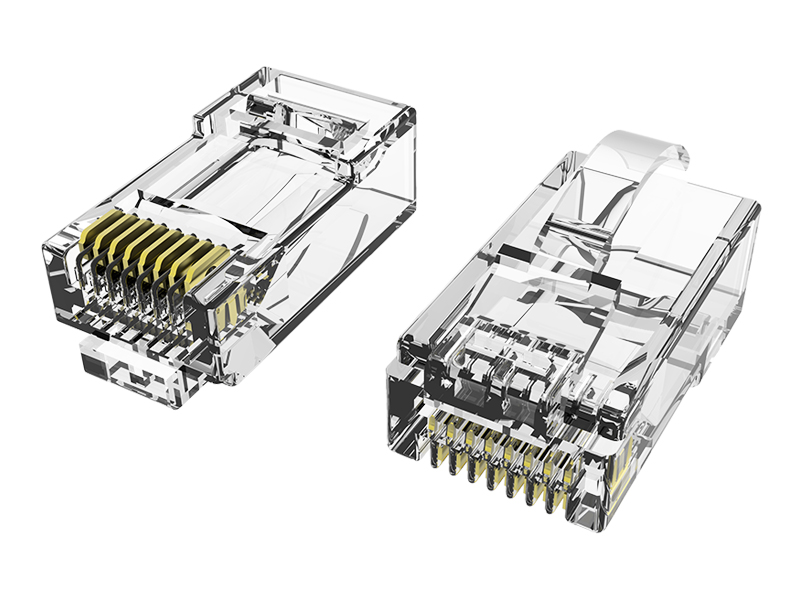
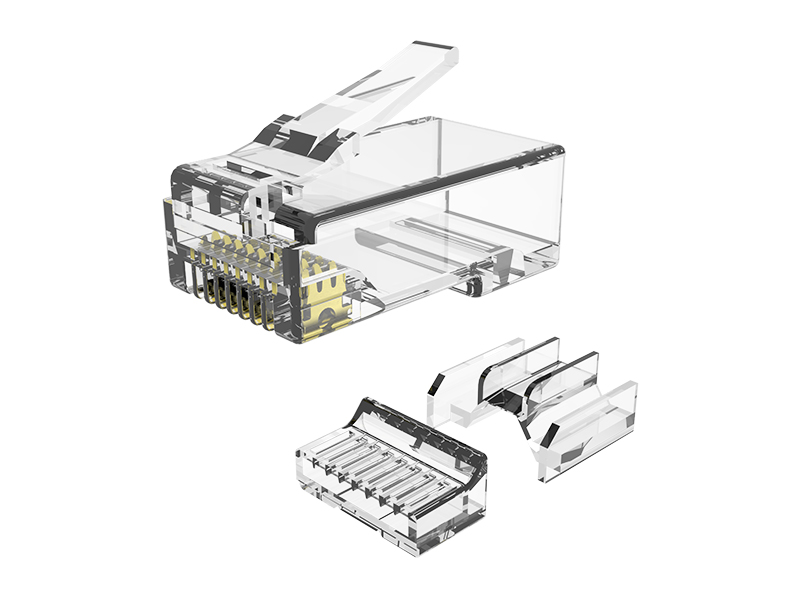
Here's a clear breakdown of the differences between standard RJ45 plugs and field termination plugs:
| Comparison Aspect | Standard RJ45 Plugs | Field Termination Plugs |
| Core Design Purpose | Factory or field-crimped for patch cords. | Field-installed permanent endpoint links. |
| Installation Method | Crimp contacts pierce wires (requires crimping tools). | IDC punch-down terminals (like keystone jacks, needs punch-down tools). |
| Internal Structure | Metal contacts only; no signal conditioning. | Often integrate signal-compensating PCBs inside housing. |
| Reusability | Single-use; damaged wires require full replacement. | Many models allow re-punching wires if termination fails. |
| Shielding Support | Shielded versions exist but require meticulous foil handling. | Optimized for shielded cables with integrated 360° metal shrouds. |
| Performance Target | Patch cord standards (TIA short-channel). | Meet permanent link standards (e.g., TIA MPTL for direct device connects). |
| Key Applications | • Work area jumpers • Equipment patch cords. | • PoE cameras/APs (direct cable-to-device) • Industrial machinery.• Outdoor permanent endpoints. |
| Durability Focus | Rated for frequent plugging/unplugging. | Built for vibration/moisture resistance (industrial variants: IP67). |
| Space Requirements | Compact; fits any Ethernet port. | Bulkier due to PCB/strain relief; may obstruct adjacent ports. |
| Cost & Skill | Low-cost; basic technician skill required. | Higher cost per unit; requires trained termination technique. |
Crucial Practical Differences
-
Signal Integrity:
- RJ45: Prone to crosstalk in long/fast links; relies on cable quality.
- Field Plug: PCB actively corrects interference for 10Gbps stability.
-
Failure Points:
- RJ45: Exposed untwisted wires at crimp point cause impedance spikes.
- Field Plug: Maintains wire twist up to terminals; minimizes untwisting.
-
Industrial Use:
- RJ45: Avoid in sustained-vibration environments (contacts loosen over time).
- Field Plug: Locking collars/strain clamps prevent cable pullout.
-
Topology Role:
- RJ45: Used between devices (transient link).
- Field Plug: Acts as final endpoint (permanent link).



 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch عربى
عربى