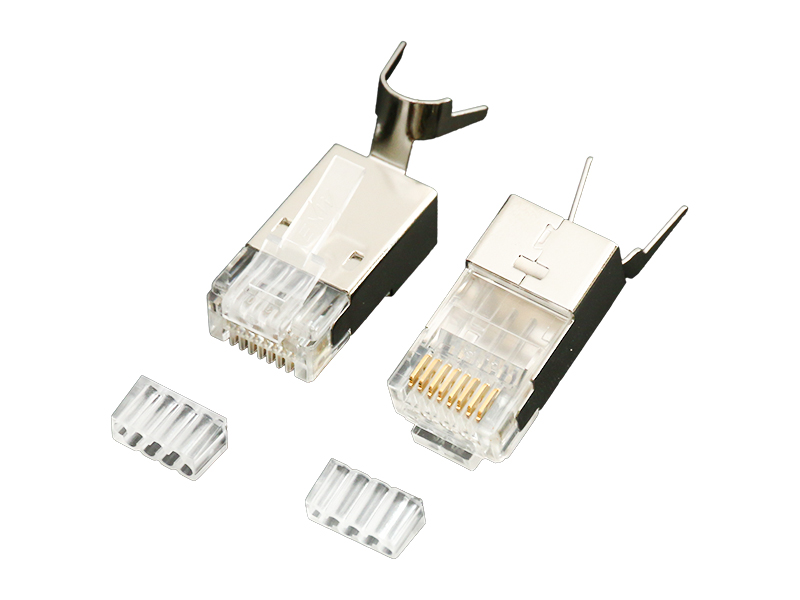
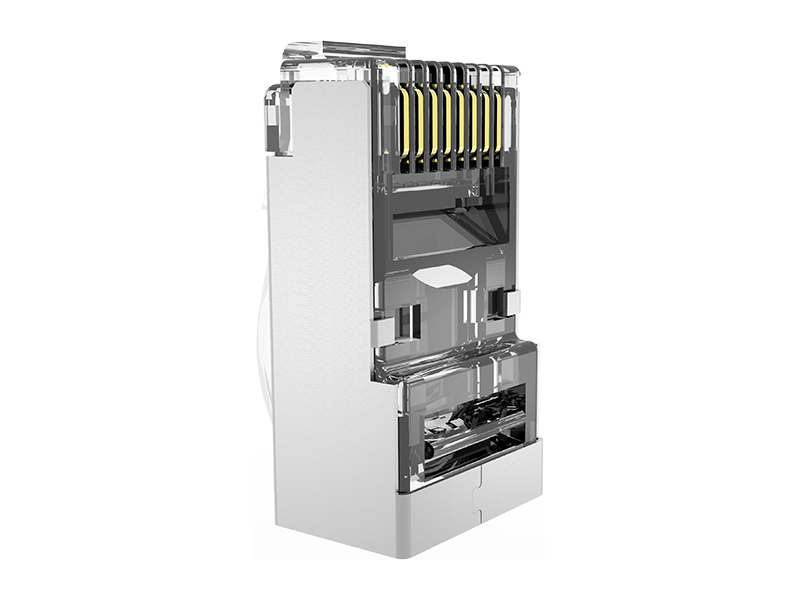
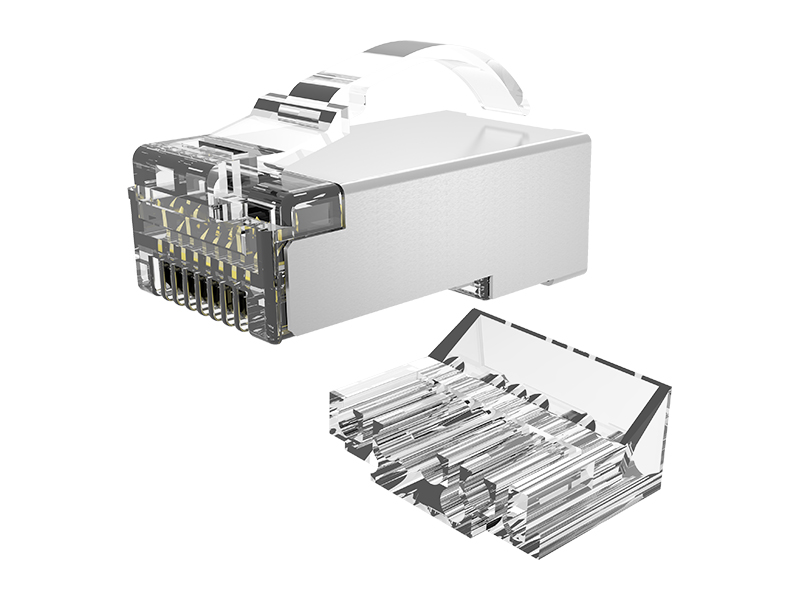
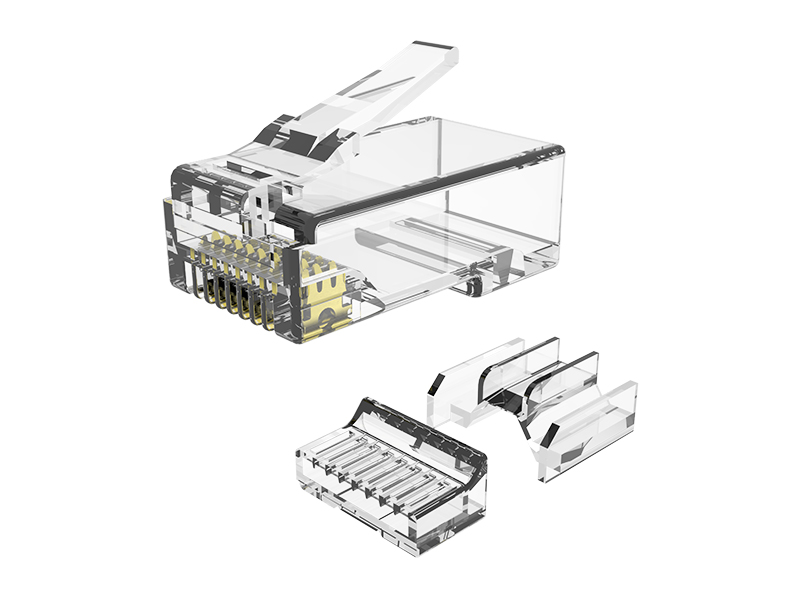
1. Applicability analysis
Design differences:
Field termination plugs (such as industrial terminals and wiring terminals) are usually used for power transmission or simple signal connections, and their structure may lack the shielding, impedance matching, and other characteristics required for high-frequency data transmission.
Data transmission (such as Ethernet, USB, RS485) requires strict signal integrity, and ordinary terminal plugs may introduce interference or signal attenuation.
Available scenarios:
Low speed signals (such as switch values and relay controls) can be temporarily used, but reliable contact must be ensured.
Short distance, low-speed data (such as RS232, 4-20mA analog signals) may be barely feasible, but the stability is poor.
2. Key risks
Signal distortion:
Unshielded terminal plugs are susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI), leading to data errors and packet loss.
Impedance mismatch may cause signal reflection, affecting high-speed communication (such as 100Mbps/Gigabit Ethernet).
Contact issues:
The contact resistance of ordinary plugs is unstable, which may cause intermittent disconnection and affect real-time data transmission.
The plug-in life is limited, and it is easy to loosen after frequent operation, which is not suitable for dynamic connection scenarios (such as mobile devices).
3. Alternative solutions
Specialized data connector (recommended):
Such as RJ45 (Ethernet cable), DB9 (serial port), M12 (industrial Ethernet), etc., specially designed for signal optimization, with shielding and locking structures.
Temporary emergency plan:
If it is necessary to use, the transmission distance should be shortened to avoid high-frequency signals, and the line shielding should be strengthened (such as wrapping copper foil).
4. Conclusion
Power/Simple Control Signal: Can be used temporarily, but ensure a secure connection.
High speed/stable data transmission: prohibited from use, must switch to a professional data interface.
Critical system: Any unreliable connection may cause communication failure, and should be selected strictly according to specifications.
| Aspect | Considerations | Risks & Limitations | Recommendations |
| Design Purpose | Typically built for power transmission or basic signal wiring (e.g., terminal blocks). | Lacks features for high-speed data: shielding, impedance control, or precise contact spacing. | Avoid for high-frequency/high-speed data (e.g., Ethernet, USB). |
| Signal Integrity | May work for low-speed signals (e.g., RS232, 4-20mA, relay control). | Unshielded designs introduce EMI/RFI noise; impedance mismatch causes signal reflection. | Use only for short-distance, low-bandwidth applications with stable connections. |
| Contact Reliability | Contacts prioritize mechanical strength over low/stable resistance. | Intermittent connections, data packet loss, or voltage drops due to poor contact. | Not suitable for real-time or critical data systems (e.g., industrial networks). |
| Durability | Designed for infrequent reconnections; higher insertion force. | Frequent plugging/unplugging accelerates wear, increasing failure risk. | For dynamic use (e.g., test equipment), choose connectors rated for high mating cycles. |
| Temporary Workarounds | In emergencies, may serve as a stopgap for non-critical data links. | Performance degrades with distance, noise, or vibration. | Add shielding (e.g., copper tape) and minimize cable length if forced to use. |
| Preferred Alternatives | Dedicated data connectors (RJ45, M12, DB9) ensure signal fidelity and robustness. | Field-terminated connectors cannot match their precision or noise immunity. | Always opt for data-grade connectors (shielded, impedance-matched) for reliable transmission. |



 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch عربى
عربى