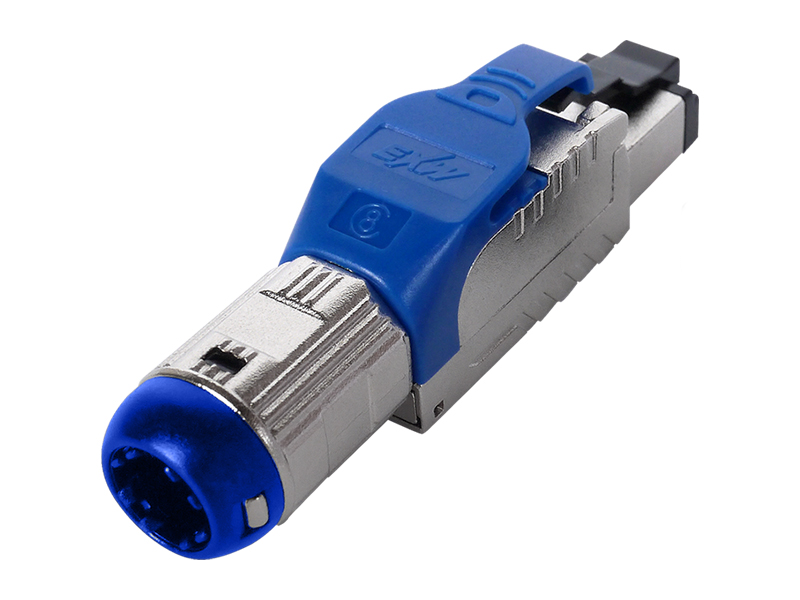
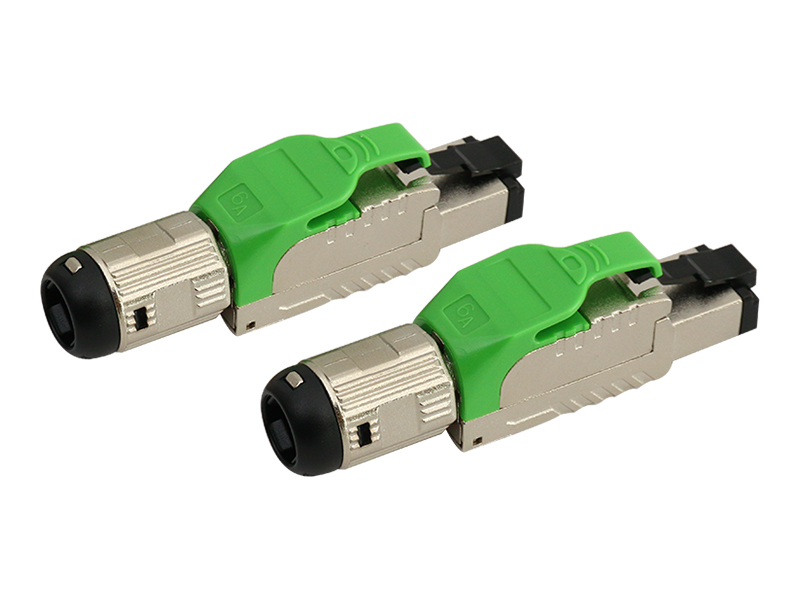
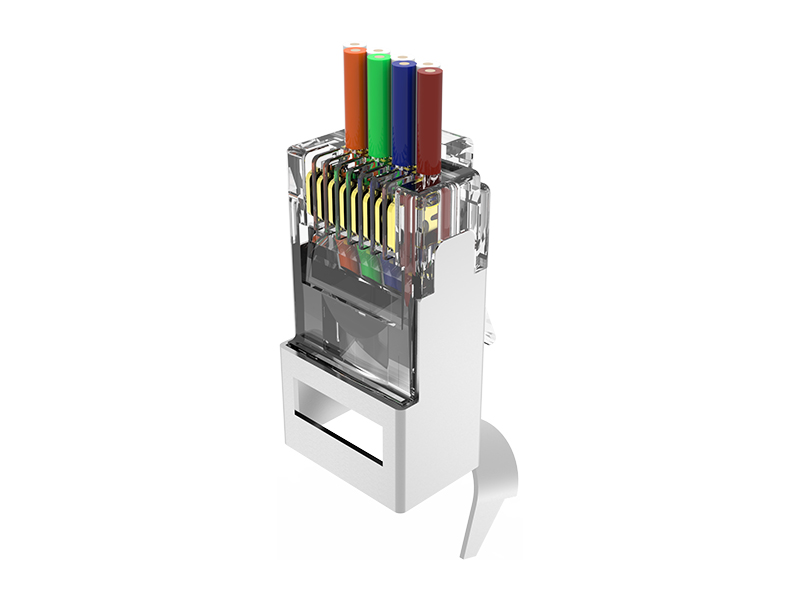
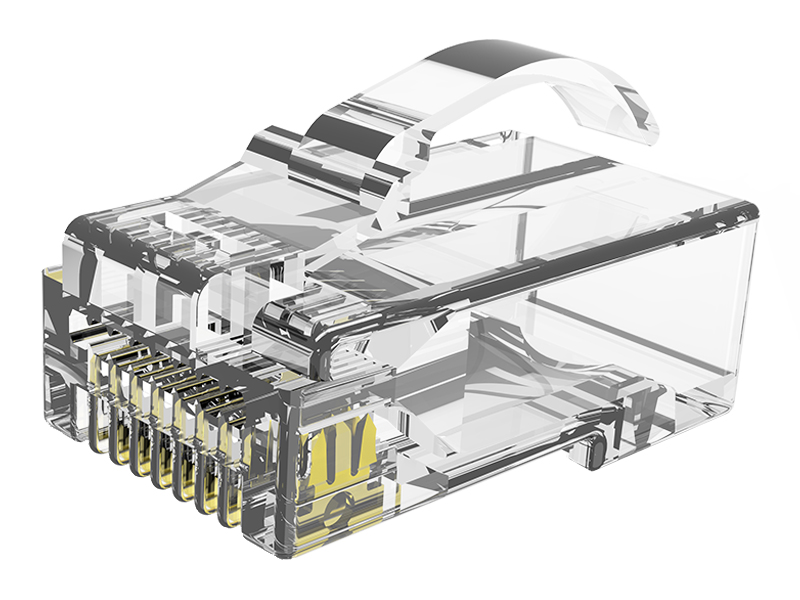
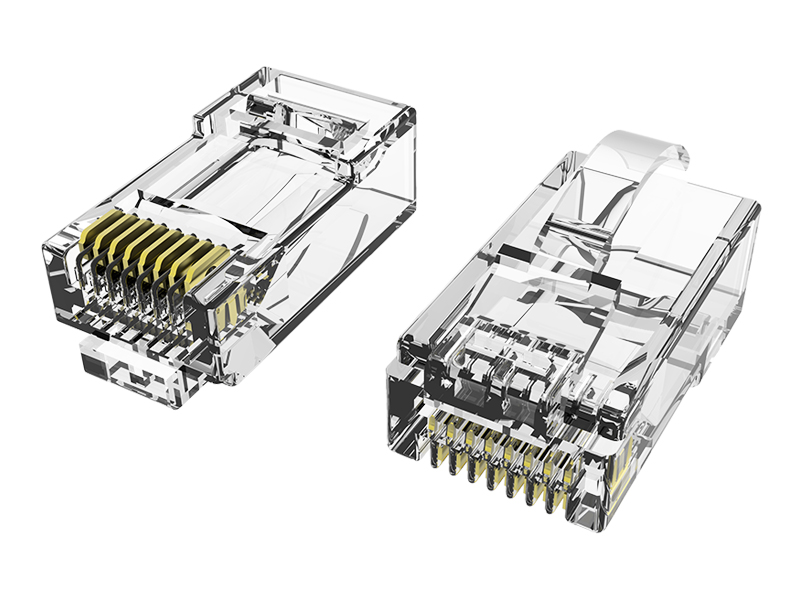
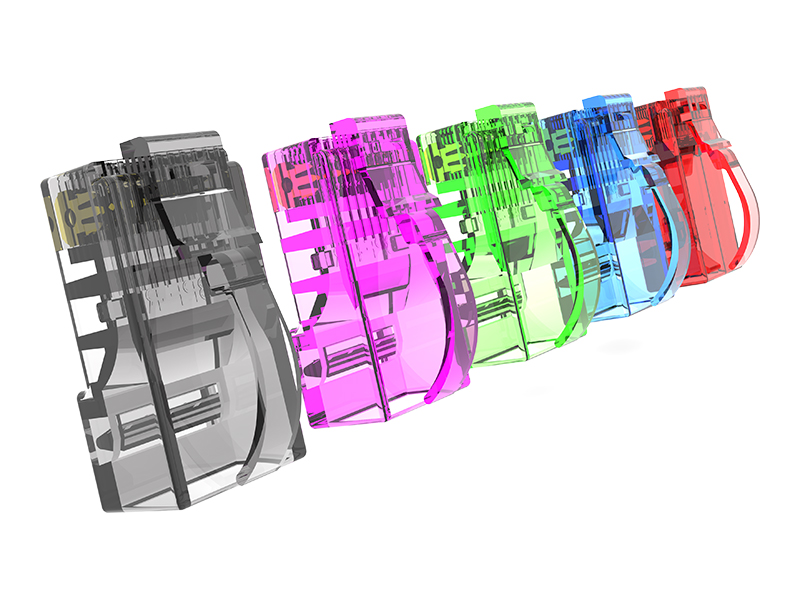
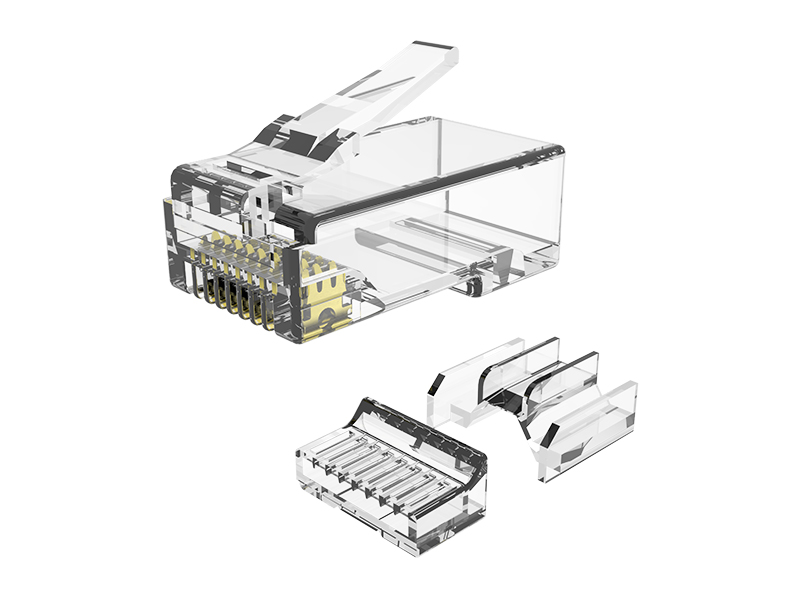
Fat OD Modular Plug Explained
1. Core Definition & Purpose
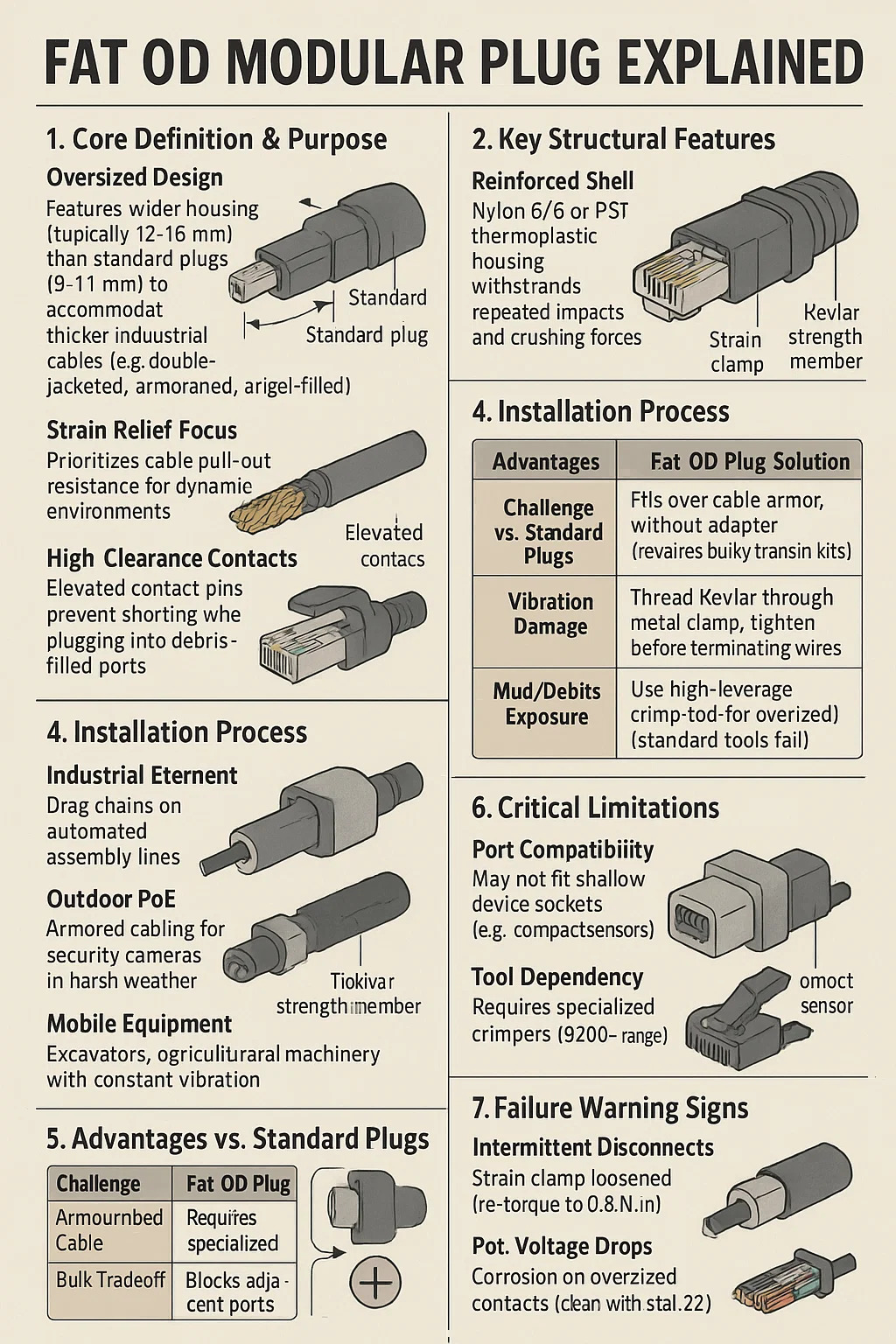
Oversized Design: Features a wider housing (typically 12–16mm diameter) than standard plugs (9–11mm) to accommodate thicker industrial cables (e.g., double-jacketed, armored, or gel-filled).
Strain Relief Focus: Prioritizes cable pull-out resistance for dynamic environments (robotics, conveyors, heavy machinery).
2. Key Structural Features
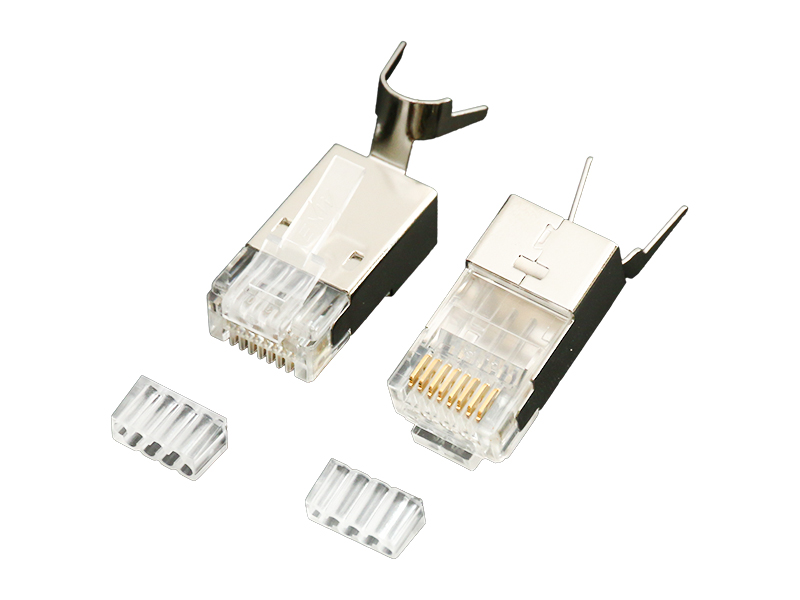
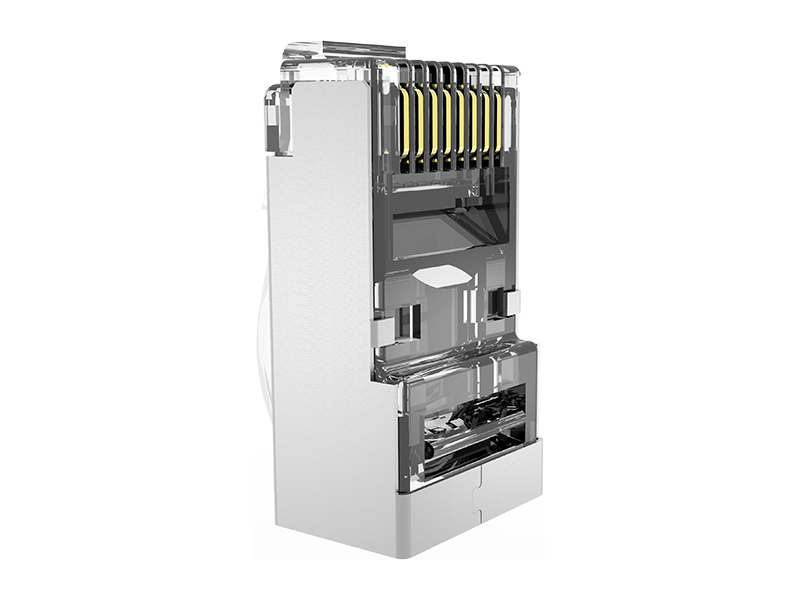
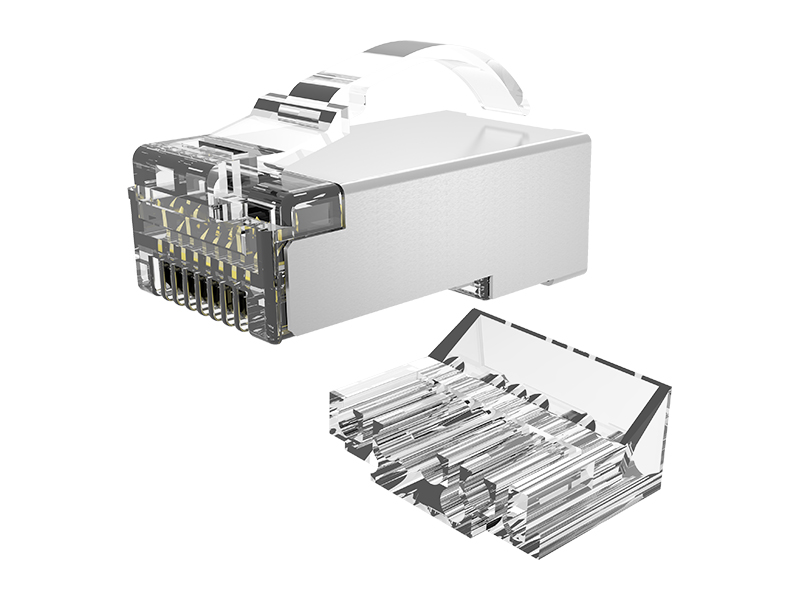
Reinforced Shell:
Nylon 6/6 or PBT thermoplastic housing withstands repeated impacts and crushing forces.
Dual-Point Strain Clamp:
Metal teeth grip cable jacket + Kevlar strength member separately.
High-Clearance Contacts:
Elevated contact pins prevent shorting when plugging into debris-filled ports.
3. Typical Applications
Industrial Ethernet:
Drag chains on automated assembly lines.
Outdoor PoE:
Armored cabling for security cameras in harsh weather.
Mobile Equipment:
Excavators, agricultural machinery with constant vibration.
4. Installation Process
Cable Prep:
Strip outer jacket to expose 40–50mm length (reveals strength member + conductors).
Strength Member Lock:
Thread Kevlar through metal clamp; tighten before terminating wires.
Termination:
Use high-leverage crimp tool for oversized contacts (standard tools fail).
5. Advantages vs. Standard Plugs
| Challenge | Fat OD Plug Solution | Standard Plug Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Armored Cable Routing | Fits over cable armor without adapter | Requires bulky transition kits |
| Vibration Damage | Dual clamping prevents conductor fatigue | Wires snap at contact points |
| Mud/Debris Exposure | Elevated contacts avoid ground shorts | Debris bridges contacts |
6. Critical Limitations
Port Compatibility:
May not fit shallow device sockets (e.g., compact sensors).
Tool Dependency:
Requires specialized crimpers ($200+ range).
Bulk Tradeoff:
Occupies 2–3× more space than RJ45; blocks adjacent ports.
7. Failure Warning Signs
Intermittent Disconnects: Strain clamp loosened (re-torque to 0.8 N·m).
PoE Voltage Drops: Corrosion on oversized contacts (clean with stabilant 22).
Cable Jacket Slippage: Kevlar not secured in metal teeth.



 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch عربى
عربى