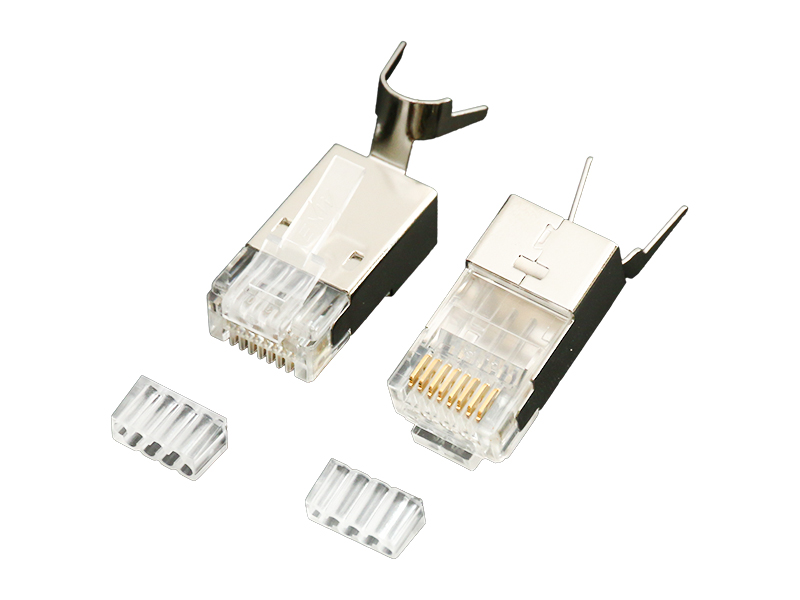
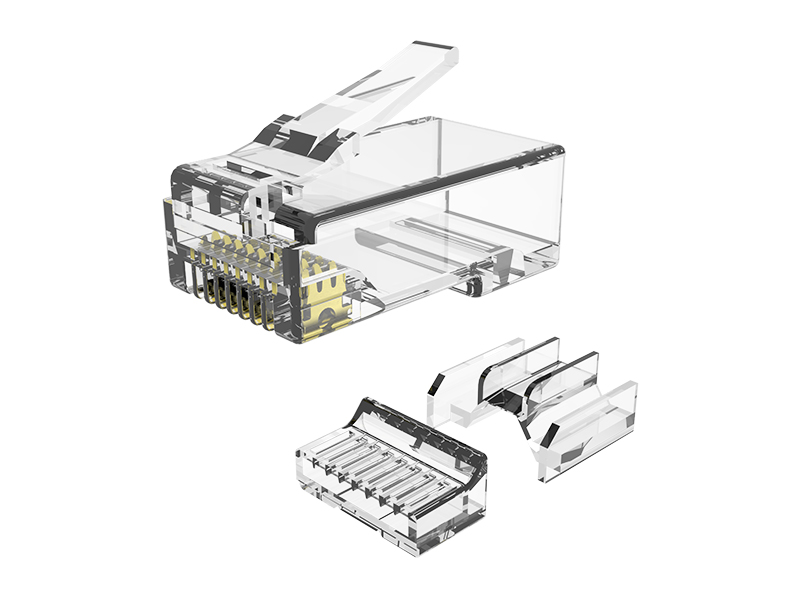
The contacts of the pass through connector need to be checked regularly. The following are key inspection points:
Contact function inspection
The contact piece is the core component for transmitting current, and its conductivity and contact stability need to be carefully checked. After long-term use, the metal contact surface may experience oxidation, wear, or accumulation of foreign objects, leading to increased contact resistance, heating, and even circuit breaking. During inspection, it is necessary to observe whether the contact area is clean, whether there are burn marks, and confirm that appropriate contact pressure and tightness are maintained during insertion and removal.
Insulation state inspection
Aging, contamination, or moisture of insulation components can pose a risk of electrical leakage or short circuit. It is necessary to check whether the insulation shell has cracks, carbonization marks, and whether the surface has accumulated dust, oil stains, or conductive impurities. Especially in humid and dusty environments, insulation performance is prone to decline, and protection needs to be strengthened.
Fixed reliability check
Loose connectors can cause power outages or structural disintegration. It is necessary to confirm whether the shell locking device (such as buckles, screws) is firm and not deformed, and whether the installation bracket is displaced or broken. If the shell is found to be damaged, the coating peeling off, or the locking force is abnormal (such as too tight/too loose), it should be replaced in a timely manner.
Operating standards and safety
The inspection should be carried out by professional personnel after cutting off the power to avoid electric shock caused by live operation. Only use original spare parts during maintenance, non certified parts may cause malfunctions or safety accidents. Insulation protective equipment (such as gloves and goggles) should be worn during operation.
| Inspection Aspect | Key Focus Areas | Critical Risks | Maintenance Guidance |
| Contact Function | Conductivity, contact stability. Check for oxidation, wear, debris buildup, burning marks. Verify contact pressure & mating tightness. | Increased contact resistance, overheating, intermittent connection, open circuit. | Clean contact surfaces meticulously. Replace contacts showing significant damage. |
| Insulation Condition | Integrity & cleanliness of insulating components. Check for cracks, carbonization, dust, oil/grease, moisture ingress. | Electrical leakage, tracking, short circuits (phase-to-phase/phase-to-ground). | Clean with approved agents only. Replace degraded/cracked insulators immediately. |
| Mechanical Security | Housing integrity. Locking mechanisms (latches, screws), mounting hardware, shell damage/corrosion. | Connector loosening, vibration damage, complete disconnection, structural failure. | Ensure proper mating/locking engagement. Replace damaged shells & hardware. |
| Safety & Procedure | Essential Requirement: Power isolation before inspection. Use OEM-approved parts only. Wear appropriate PPE (insulated gloves/safety glasses). | Electric shock, arc flash, equipment damage, introducing incompatible parts. | Follow documented Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedures strictly. Never bypass safety protocols. |
Notes:
- Regular inspection is mandatory to prevent failures and ensure operational safety/reliability.
- Frequency depends heavily on the operating environment (e.g., vibration, dust, humidity, chemicals) and electrical duty cycle (e.g., high current/voltage).
- High-voltage applications demand stricter adherence to safety procedures and potentially more frequent inspections.



 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch عربى
عربى